Can Green Card Holders Vote?
Quick Answer: In the United States, only U.S. citizens who meet the required age and residency conditions can vote. Typically, those holding green cards are excluded from participating in federal elections, though certain states may grant the right to vote in local and state elections. Voting in a federal election by a green card holder can result in deportation and can jeopardize prospects for citizenship. If an individual has mistakenly registered or cast a vote while ineligible, it is crucial to consult with legal counsel to rectify the situation prior to pursuing citizenship.
In the United States, Lawful Permanent Residents (LPRs)—often known as green cardholders—have access to many privileges and rights, akin to those enjoyed by American citizens. However, in most cases, voting is an exception to these rights.
In essence, the rules surrounding the voting rights of green card holders are clear on the federal level, where it’s generally never permitted. However, at a state and local level, voting rights for lawful permanent residents are a bit more nuanced and contingent upon multiple factors.
For instance, some locales and states permit voting by LPRs, provided specific conditions are fulfilled (which you’ll learn about further below).
Acquiring comprehensive knowledge of the laws governing your respective state is crucial before attempting to vote, as unauthorized registration or voting can lead to serious repercussions.
What is voting?
Voting in the USA is a constitutional right and democratic process that allows eligible citizens to participate in the selection of their representatives at various levels of government, or express their opinion on specific legislation, policies, or referenda.
Federal Level:
At the federal level, eligible voters can cast their votes to elect:
- The President and Vice President of the United States (every four years).
- Members of the U.S. House of Representatives (every two years).
- U.S. Senators (every six years, staggered terms).
State and Local Levels:
At the state and local levels, voting can include electing governors, mayors, and other local officials and deciding on state and local laws, policies, and initiatives.
Voting can be done in various ways, including in-person voting on Election Day, early voting, absentee voting, and mail-in voting, depending on the provisions of each state. In summary, voting is a fundamental civic duty and a mechanism for citizens to express their will and contribute to the shaping of their government and legislation in the USA.
Who Can Vote in the USA?
To be eligible to vote, individuals must typically be:
- U.S. citizens.
- At least 18 years old on or before Election Day.
- Residents of the state where they are voting.
- Registered to vote by their state’s voter registration deadline.
Restrictions:
Certain legal and procedural restrictions apply, and individuals convicted of felonies or mentally incapacitated may be ineligible to vote, depending on state laws.
Can You Vote With A Green Card?
Green card holders, or lawful permanent residents, are not allowed to vote in federal elections in the United States. Voting in federal elections as a green card holder can lead to severe consequences, including deportation and jeopardizing the ability to become a U.S. citizen.
However, some local jurisdictions do allow green card holders to vote in local elections, but these are exceptions and not the general rule. Always check local laws before attempting to vote as a green card holder.
What States Can Green Card Holders Vote at Local Elections?
As of June 2023, the District of Columbia along with cities in three states—California, Maryland, and Vermont—have granted noncitizens the right to participate in select or all local elections, including those for school board, mayor, and other municipal roles.
California
Oakland: A charter amendment approved in 2022 allows noncitizens who are parents, legal guardians, or caregivers of a child to vote in the Office of Oakland School Board Director elections, effective in 2023. Click here to learn more.
San Francisco: A 2016 amendment allowed noncitizens of legal voting age and with a child in the San Francisco Unified School District to vote in Board of Education elections. However, in July 2022, this law was ruled unconstitutional, being in violation of the California Constitution. Click here to learn more.
District of Columbia
In October 2022, the District of Columbia Council enacted the D.C. Noncitizen Vote Act, allowing noncitizens to vote in local elections. After overcoming opposition, it passed its congressional review in March 2023. However, it is under ongoing litigation as of June 2023 due to a filed lawsuit seeking an injunction to prevent the law’s enforcement.
Maryland
The state constitution allows municipalities the autonomy to permit noncitizens to vote in local elections. Several Maryland municipalities including Barnesville, Cheverly, Chevy Chase Section 3, Garrett Park, Glen Echo, Hyattsville, Martin’s Additions, Mount Rainier, Riverdale Park, Somerset, and Takoma Park have provisions allowing noncitizens to participate in local elections under specific conditions.
Vermont
In Montpelier and Winooski, Vermont, noncitizens are allowed to vote in local elections due to city charter amendments enacted into law on June 24, 2021, even after the Governor’s veto was overridden by the state legislature.
Noncitizen Suffrage in Local Elections:
“Noncitizen suffrage in local elections” means some places allow noncitizens to vote in local elections, typically for positions or issues only affecting the local municipality, but not in state or federal elections. The eligibility and conditions for this vary by jurisdiction.
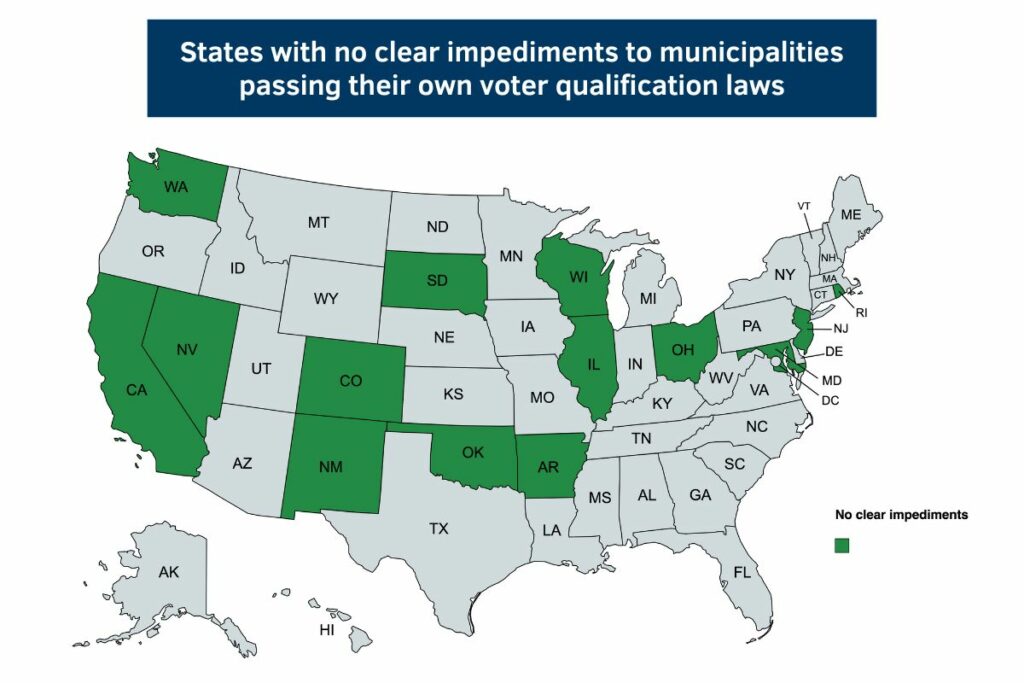
Joshua A. Douglas, an Associate Professor of Law at the University of Kentucky College of Law, conveyed in a 2017 article, “Provided there are no explicit prohibitions in state constitutions or legislation, municipalities hold the authority to broaden voting rights in local elections under the principle of home rule.”
Douglas listed 14 states, California and Maryland included, where no distinct barriers prevent municipalities from enacting their own voter qualification statutes:
The following list outlines the cities that extend voting privileges to non-citizens.
In some states, modifications to local charters necessitate approval from state legislatures, restricting municipal control over voter eligibility laws, while others do not impose such constraints.
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Illinois
- Maryland
- Nevada
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Rhode Island
- South Dakota
- Washington
- Wisconsin
Source: Stay up-to-date and learn more about non-citizen voting here
Source: Joshua A. Douglas, University of Kentucky
What happens if a green card holder votes?
Voting as a non-citizen green card holder in U.S. elections can have severe consequences. Here are several repercussions that may arise:
1. Deportation:
Green card holders who vote unlawfully can be deemed removable (deportable) under immigration law, potentially leading to deportation.
2. Ineligibility for Naturalization:
Non-citizen voting can result in a person being found to lack good moral character, which is a requirement for naturalization. This may impede the ability to become a U.S. citizen.
3. Criminal Penalties:
Unlawful voting is a federal crime and can result in fines and/or imprisonment.
4. Inadmissibility:
Individuals who have voted unlawfully may be considered inadmissible, which could prevent them from re-entering the United States if they travel abroad or from adjusting their immigration status.
5. Impact on Future Immigration Benefits:
Unlawful voting can affect the eligibility for future immigration benefits, including visa renewals, adjustments of status, or other immigration reliefs.
6. Rejection of Citizenship Application:
When applying for U.S. citizenship, unlawful voting can lead to the rejection of the naturalization application.
7. Permanently Barred from U.S. Citizenship:
In some severe cases, if a non-citizen falsely claims to be a U.S. citizen to vote, they can be permanently barred from becoming a U.S. citizen.
According to official US government sources:
“Any person who violates this section shall be fined under this title, imprisoned not more than one year, or both.’’
Govinfo – Public Law
Legal Counsel and Rectification:
- Seek Legal Advice: Non-citizens who have registered or voted unlawfully should consult with an immigration attorney to discuss possible legal remedies and understand the implications on their immigration status.
- Rectification Measures: In certain situations, rectification measures like canceling voter registration or notifying the appropriate election officials about the mistake can mitigate the repercussions, but it’s important to do this under legal counsel to avoid self-incrimination.
In essence, any non-citizen, including green card holders, should refrain from participating in elections where they are not eligible to vote and should seek legal counsel if they have done so in error to mitigate potential severe consequences.

Green Card Holder Voting FAQs
If you are a non-citizen who has voted in a U.S. election, consulting an immigration attorney is crucial. They can provide appropriate guidance on the necessary steps to mitigate any potential repercussions, especially before applying for citizenship, to avoid unforeseen hindrances in acquiring naturalized U.S. citizenship.
Regrettably, mere registration to vote can create serious complications, potentially leading to denial of citizenship or deportation. However, this error can be rectified. It is essential to promptly remove your name from the voter registration list by notifying your County Auditor’s Office. Remember, unintentional registration, such as through motor-voter laws during driver’s license applications or receiving public assistance, also necessitates immediate correction.
As of the latest available information, green card holders cannot vote in New York City municipal elections. Although legislation (Int. 1867-2020) was initially approved by the New York City Council on December 9, 2021, to grant voting rights in municipal elections to lawful permanent residents and other non-citizens authorized to work in the United States, this law was later overturned on June 27, 2022, by the New York State Supreme Court for Staten Island. The court ruled that the law violated the state’s constitution, as it did not expressly include non-citizens in the provision for voting rights. Source.
No, green card holders cannot vote for state governor as voting in such elections is typically reserved for U.S. citizens.
U.S. citizens can vote in federal, state, and most local elections, run for elected office, apply for federal employment and benefits, travel with a U.S. passport, and are afforded certain protections abroad. Green card holders are generally ineligible for these privileges.
Green card holders have the right to live and work permanently in the U.S., own property, attend public schools, colleges, and universities, and join certain branches of the U.S. Armed Forces. They are also afforded legal protections under U.S. law.

Summary: Voting & Green Card Holders
In conclusion, while green card holders enjoy numerous privileges and rights in the United States, participating in federal elections is not among them, and participating unlawfully can have severe repercussions, including deportation and jeopardizing future citizenship.
However, the landscape is varied and dynamic at the local level, with some municipalities extending the right to vote in local elections to non-citizens, reflecting a nuanced approach to civic participation by lawful permanent residents.
Although initiatives like those in New York City have faced legal challenges and reversals, they highlight the ongoing discourse and evolving perspectives on the role and rights of green card holders in the American democratic process. The complexities and variances in laws underscore the importance of staying informed and adhering strictly to the legal provisions governing voting rights in one’s jurisdiction.








